A bullet leaves a rifle with a muzzle velocity of 521 m/s. While accelerating through the barrel of the rifle, the bullet moves a distance of 0.840 m. Determine the acceleration of the bullet (assume a uniform acceleration).
An engineer is designing a runway for an airport. Several planes will use the runway and the engineer must design it so that it is long enough for the largest planes to become airborne before the runway ends. If the largest plane accelerates at 3.30 m/s

2025.10.07 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Candy corn: yay or nay?
: Candy corn: yay or nay?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Do Now - packet page 21 & 22
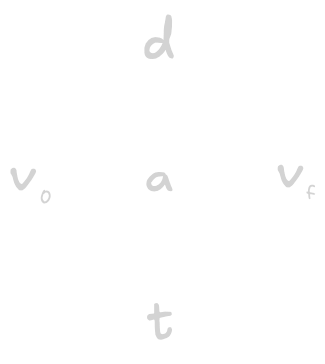
- Introduction to kinematic equations and the cross diagram
- Practice with equations & problem-solving
 Goals
Goals


 Upcoming
Upcoming
- PC Velocity Graphs due Wed
- PC Kinematic Eqns due Thu
- Quiz Thursday
 2025.10.03 Regents Physics
2025.10.03 Regents Physics 
 of the
of the  : WYR visit a corn maze or haunted house?
: WYR visit a corn maze or haunted house?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Packet pages 13 - 16
- Stop at question 4 on page 16
- Review and New - VT Graphs
- Finish Page 16, 21-22
 Goals
Goals

 Homework Due Wednesday
Homework Due Wednesday
- Velocity Time Graphs 1
- Velocity Time Graphs 2
 2025.10.02 Regents Physisc
2025.10.02 Regents Physisc 
 of the
of the  : Your favorite halloween costume?
: Your favorite halloween costume?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Finish Card Sort Data collection
- Card Sort Summary Chart & Discussion
- While waiting...Physics Classroom:
- Graph that Motion
- Name that Motion
- Match that Graph
 Goals
Goals

 Homework
Homework
Finish Physics Classroom Practice Assignments
 2025.10.01 Regents Physics
2025.10.01 Regents Physics 
 of the
of the  : Cake or pie?
: Cake or pie? 

 Agenda
Agenda
- Card Sort
- Summary Table as a class
- Start Physics Classroom Practice
- Name that Motion
- Graph that Motion
 Goals
Goals

 Homework
Homework
- PC: Name That Motion
- PC: Match That Graph
Card Sort
There 8 Verbal Descriptions:
- Match 1 Position vs. time and 1 Velocity vs. Time graph to each verbal description
- Sketch the graphs with the description in your lab note as a hypothesis column
- Connect the smart cart to your computer in graphical analysis and record the data
- record this as your data next to your hypothesis
- Double check all representations with my website:
- Draw the motion map from the website below your graphs
- Fill out summary chart
Fill out chart on whiteboard
If it is increasing (
- Constant speed +
- Constant speed -
- Speed up +
- Speed up -
- Slow down +
- Slow down -
- Slow down + speed up -
- Slow down - speed up +
| # | xt slope | v values | vt slope | accel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. |  + + |
 + + |
 0 0 |
 0 0 |
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 8 |
2025.09.29 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Would you rather watch a movie on your TV at home or on the big screen in the theater, and why?
: Would you rather watch a movie on your TV at home or on the big screen in the theater, and why?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Board Meeting -> Does it change velocity?
- Linearization
- how is x related to t?
- how is v related to x?
- Finish Up Lab Notebook
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
2025.09.26 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : What is your favorite road trip snack?
: What is your favorite road trip snack?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Quiz
- Finish Wheel Lab Data Analysis
- Wheel Lab Board Meeting
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
2025.09.25 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : What is your favorite family vacation?
: What is your favorite family vacation?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Wheel Lab
-> introduction and observations
-> Technology pieces - Wheel Lab -> Collect Data
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
- HW: Finish Red Car vs Green Car on PC (due Friday)
- Quiz Friday
2025.09.23 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : What is the worst food?
: What is the worst food?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Red Car vs. Green Car: Team problem-solving
- Solve in group
- Share solutions
- Dueling Buggies Lab
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
- HW: Finish Red Car vs Green Car on Physics Classroom (due Friday)
- Quiz Friday
Team Solving
Solve with your lab group on a whiteboard
A red car (on left) and a green car (on right) are spaced
Dueling Buggies Lab
Lab Question
How can we use measurements and models to predict the meeting point of two battery-powered buggies, one fast and one slow, when they move toward each other from known starting positions?
Lab Purpose
To determine and test the predicted meeting point of two buggies moving at constant, but different, speeds toward each other, using measurements, motion maps, graphs, and algebraic models.
Procedure Overview
- In teams, measure all properties you think are necessary to predict how the fast and slow buggies will move (speed, direction, etc.).
- Record your measurements and describe your methods.
- After measurements, your buggies will be collected. The teacher will mark two starting lines: one for the fast buggy and one for the slow buggy.
- Using your data, determine and clearly mark on the floor where you predict the two buggies will meet if started at the same time.
Procedure Overview
- Use at least two different approaches (motion maps, position-time graphs, algebraic equations, etc.) to support your prediction.
- Once you have made your prediction, test it by running the buggies from the assigned start lines.
- Record and analyze the outcome.
Data Section
- Table of measurements for each buggy (speed, direction, other relevant properties)
- Sample calculations for determining speed
- Sample calculations for determining speed
- Diagrams, graphs, or descriptions of any modeling tools used
- Sketches or descriptions of motion maps and position-time graphs
- Written description of your prediction process
Dueling Buggies Lab
Lab Question
How can we use measurements and models to predict the meeting point of two battery-powered buggies, one fast and one slow, when they move toward each other from known starting positions?
Lab Purpose
To determine and test the predicted meeting point of two buggies moving at constant, but different, speeds toward each other, using measurements, motion maps, graphs, and algebraic models.
2025.09.22 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : If you were to open a store, what would you sell?
: If you were to open a store, what would you sell?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Finish Walk the Graph Lab
- Velocity vs. time graphs
- Red Car vs. Green Car
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
 Open Graphical Analysis
Open Graphical Analysis
Click link in slides or find herehttps://graphicalanalysis.app/
 Save this to your bookmarks
Save this to your bookmarks
2025.09.19 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Would you rather be a superhero or super villain?
: Would you rather be a superhero or super villain?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Find Graphical Analysis Page
- Motion Maps
- Walk the Graph Lab
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
Walk the Graph Lab 
Question: How can different types of walking motion be represented and interpreted using position-time and velocity-time graphs?
Purpose: To investigate how various walking motions (such as walking away from or toward the sensor, walking at different speeds, or stopping and starting) are represented on position-time and velocity-time graphs, and to develop an understanding of the relationship between motion and its graphical representation.
Instructions for Lab Notebook Reflection:
Record your answers to the reflection questions above in your lab notebook. Include sketches of your graphs and a brief written description of your movement for each trial.
2025.09.17 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Would you rather live in the ocean
: Would you rather live in the ocean  or on the moon
or on the moon  ?
?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Do Now PC - Position-Time Graphs - Conceptual Analysis Concept Builder
- Average vs. Instantaneous
- Position-Time Graphs - Numerical Analysis
- Motion Maps
 Goals
Goals


 Homework
Homework
- PC: CalcPad - Kinematics 2: Position-Time Graphs
2025.09.16 Do Now
1. Complete Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement Worksheet
2. Provide an example where distance, displacment, and final position are the same
3. Provide an example where distance, displacment, and final position are different
2025.09.16 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : What's the best pizza topping?
: What's the best pizza topping? 
 Agenda
Agenda
- Do Now
- Speed vs. Velocity
- Describing Motion
- Average vs. Instantaneous Speed & Velocity
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
- Physics Classroom HW:
- Set K1: Distance versus Displacement
2025.09.15 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : What is the proper length of a playlist?
: What is the proper length of a playlist?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Buggy Lab Board Meeting
- Remind yourself of your lab & results
- CV Notes & Practice
- Physics Classroom: Position-Time Graphs - Conceptual Analysis Concept Builder
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
2025.09/11 **Regents Physics **
 of the
of the  : Does a week start on Sunday or Monday?
: Does a week start on Sunday or Monday?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Finish Buggy Lab & Whiteboard Results
- Buggy Lab Board Meeting
- CV Model Notes
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
2025.09.10 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Would you rather be the hero or the sidekick?
: Would you rather be the hero or the sidekick?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Do Now: Reread/Remind yourself about Data Collection
- Discussion of Data Best Practices
- Dune Buggy Challenge
 Goals
Goals

 Upcoming
Upcoming
- Get your parent/guardian to sign the student safety contract
Dune Buggy Challenge 
Questions:
- How much time does it take a Dune Buggy car to travel a specified distance?
- Does your buggy move in a consistent manner?
Purpose:
To collect distance-time data for a Dune Buggy Car in order to predict the time it takes a Dune Buggy to travel a specified distance
Data & Prediction
- when graphing put time on the horizontal axis
2025.09.09 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Is it OK to ask the genie for infinite wishes?
: Is it OK to ask the genie for infinite wishes?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Finish Pasta Bridge Lab
- Pasta Lab Board Meeting
- Data Collection Best Practices
- Dune Buggy Challenge
 Goals
Goals


 Upcoming
Upcoming
Pasta Bridge Lab 
Objective:
- Determine the strength of a pasta bridge by finding the relationship between strength (number of marbles) and strands of pasta
- Develop an experiment to compare at least two types of pasta. Create a hypothesis for which will be stronger.
Board Meeting
Rules 
Listen
Speak Clearly
Ask Questions
Seek to understand
Refer to your board and use evidence
Use & connect multiple representations
Come to consensus
Goals 
- Practice Presenting to Class
- speaking clearly
- listening intently
- Learn how to come to class consensus
- What does the majority of the data show?
- Create a culture of learning from each other
Board Meeting
- What is the slope?
- For every statement ("The y quantity changes the slope number
for every 1 x quantity ")
- For every statement ("The y quantity changes the slope number
- What is the intercept?
- What do they represent?
- How does each group's result compare?
Pasta Bridge Model:
Data Collection 
- Go to Data Collection Best Practices Interactive
- Read and click through the examples
- Reflect on your Coefficient of Restitution lab, did you follow these practices? How can you improve upon your design?
Claim:
I predicted that it would take my Dune Buggy car _______________ to travel the specified distance of ______________ cm.
Evidence:
(Discuss values from your Data section...identifying the data that you used to determine the prediction. Use specifics in your discussion.)
Reasoning:
(Explain in a few sentences why this evidence provides logical support for believing that your claim is true. And while you’re at it, you ought to mention how well...or not well...that you did.)
2025.09.05 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Would you rather vacation in Hawaii or Alaska?
: Would you rather vacation in Hawaii or Alaska?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Pasta Bridge Lab
- Collect Data
- Graph Data
- Write Discussion and Conclusions
- Whiteboard Lab Results
- Board Meeting
 Goals
Goals


 Upcoming
Upcoming
- Safety Contract...still figuring out digital or physical
2025.09.04 Regents Physics
 of the
of the  : Sweet or savory for breakfast?
: Sweet or savory for breakfast?
 Agenda
Agenda
- Sit Anywhere
- Do Now (fill out questionnaire & card)
- Question of the Day
- Survival Island
- Pasta Bridge Lab
 Goals
Goals


 Homework
Homework
- Signed Safety Contract
Do Now
- Fill out index card:
- Name
- Phone number to reach your parents/guardians if you sleep through the Regents
- Favorite Candy
- Favorite Emoji
- Emoji the describes your current mood
- Fill out Paper Quesionnaire
Survival Island 
- Share your survival skill that you wrote down with your group
- Using everyone's skill develop a plan to survive or escape the deserted island
- On your whiteboard present your plan (drawing, mind map, set of instructions)
- Highlight everyone's skill
Surivial Plan...
Pasta Bridge Lab 
Objective:
- Determine the strength of a pasta bridge by finding the relationship between strength (number of marbles) and strands of pasta
 Lets Science!
Lets Science! 
 Lab Notebooks
Lab Notebooks 
What is a Lab Notebook?
- A detailed, chronological record of a scientist's research activities, experiments, and observations.
- Documentation of the scientific process from intial ideas to final results and conclusions.
Why keep lab notebooks?
- Document Research
- Develop Ideas
- Organize Data
- Collaboration Tool
- Publication Support
- Troubleshooting
- Intellectual Property Protection
- Historical Record
Lab Notebooks can be Legal Documents
- Proof of invention in Patent Cases
- Intellectual Property Protection
- Admissibility in court - must be properly maintained
- Note: Often property of the instituation where the research was conducted (i.e. Property of Regeneron, or Property of Cornell University)
Remember
- Lab notebooks are most importantly scientific documentation
- They represent the scientific process and are record of your thinking
- This means your ideas and conclusions and hypotheses can change based on new data
Lab Notebook
- Write in pen
- All mistakes get a
single cross through - Full Date (YYYY/MM/DD) at the beginning of each entry (for multiday labs date start of each day)
- Enter Lab Pages into table of contents
Lab Notebook - Pre Lab
-
Title and objective of the experiment:
- Write a clear, concise title for each experiment.
- State the main objective or purpose of the experiment in 1-2 sentences.
-
*Theoretical background:
- Briefly explain the relevant scientific principles.
- Include key equations or concepts that will be tested or applied.
-
Hypotheses:
- State your predictions about the experiment's outcome.
- Base these on your understanding of the theory.
Lab Notebook - Pre Lab
- Materials and equipment list:
- Provide a detailed list of all materials and equipment used.
- Include model numbers and specifications where relevant.
- Experimental procedure outline:
- Write a step-by-step outline of the planned procedure.
- Be specific enough that someone could replicate your experiment.
During the Experiment
- Raw data in tables with units:
- Create neat, organized tables for all numerical data.
- Always include units and uncertainty estimates.
- Label columns clearly and use consistent significant figures.
- Observations and qualitative notes:
- Record all relevant observations, even if they seem unimportant.
- Note any unexpected occurrences or anomalies.
During the Experiment
- Any changes to the planned procedure:
- Document any deviations from the original procedure.
- Explain why changes were made and how they might affect results.
- Sketches or diagrams of experimental setup:
- Include clear, labeled diagrams of your experimental setup.
- Add dimensions and important details to aid in replication.
Post Lab
- Data analysis and calculations:
- Show all steps in your calculations, including formulas used.
- Explain your reasoning for each step of the analysis.
- Graphs and charts:
- Create neat, properly labeled graphs and charts.
- Include titles, axis labels with units, and legends where appropriate.
Post Lab
- Discussion of results:
- Interpret your results in the context of the experiment's objectives.
- Explain any patterns or trends observed in the data
- Comparison with hypotheses:
- Explicitly state whether your results support or refute your hypotheses.
- Discuss possible reasons for any discrepancies.
- Sources of error and uncertainty:
- Identify potential sources of experimental error.
- Discuss how these might have affected your results.
- Quantify uncertainties where possible.
Post Lab
- Conclusions:
- Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
- Relate these back to the original objectives and broader scientific principles.
- Suggest improvements or future directions for the experiment.
Pasta Bridge Lab 
Objective:
- Determine the strength of a pasta bridge by finding the relationship between strength (number of marbles) and strands of pasta
- Develop an experiment to compare at least two types of pasta. Create a hypothesis for which will be stronger.
Board Meeting
Rules 
Listen
Speak Clearly
Ask Questions
Seek to understand
Refer to your board and use evidence
Use & connect multiple representations
Come to consensus
Goals 
- Practice Presenting to Class
- speaking clearly
- listening intently
- Learn how to come to class consensus
- What does the majority of the data show?
- Create a culture of learning from each other